Function In Python Programming | Python Programming
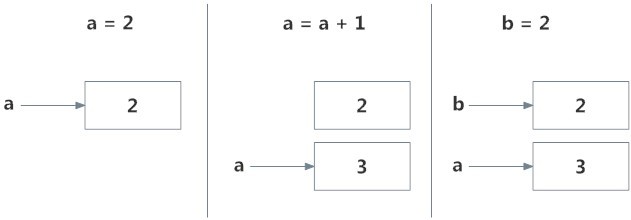
What is a function in Python? In Python, a function is a group of related statements that perform a specific task. Functions help break our program into smaller and modular chunks. As our program grows larger and larger, functions make it more organized and manageable. Furthermore, it avoids repetition and makes code reusable. You can define functions to provide the required functionality. Here are simple rules to define a function in Python. Function blocks begin with the keyword def followed by the function name and parentheses ( ( ) ). Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within these parentheses. You can also define parameters inside these parentheses. The first statement of a function can be an optional statement – the documentation string of the function or docstring . The code block within every function starts with a colon (:) and is indented. The statement return [expression] exits a function, optionally passing back an expression to the ca