Introduction To Computer System
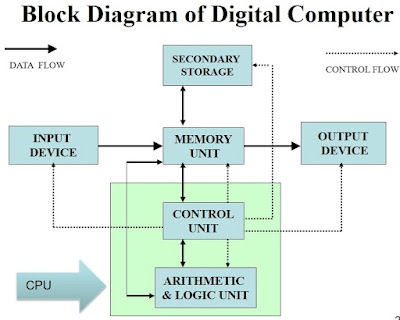
Introduction to Computer A computer is an electronic device capable of performing arithmetic and logical operations. It can also store a large volume of information . Characteristics of Computer SPEED The speed with which the computer works can be understood by the units of measurement of time within a computer. They are : MILLI SECOND – 1/1000 TH OF A SECOND MICRO SECOND – 1/1000 TH OF A MILLI SECOND NANO SECOND – 1/1000 TH OF A MICRO SECOND PICO SECOND – 1/1000 TH OF A NANO SECOND STORAGE As already discussed a computer can store a large volume of information. The factors to be considered for storage are : • RETREIVAL – IMMEDIATE • SPACE – VERY LITTLE • MEDIA – MAGNETIC MEDIA • LONGIVITY – FOR EVER ACCURACY The accuracy of the computers is consistently high. Errors in the machinery may occur, but due to efficient error-detecting techniques, these very seldom lead to wrong results. Errors in computing are due to human rather than techno