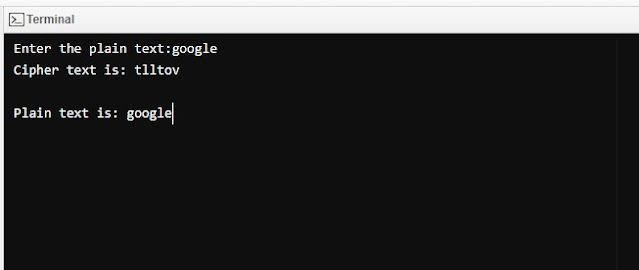
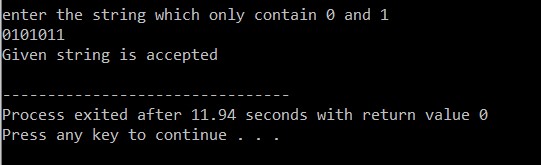
Top 10 Programming Language to learn in 2023
Are you a programming enthusiast looking to stay ahead of the curve in 2023? With the ever-evolving tech landscape, keeping up with the Best Programming Language to learn can be a daunting task. Fear not, as we have compiled a list of the top 10 Programming Languages that you should consider learning in 2023. Python: This versatile language continues to dominate in 2023, with its ease of use, readability, and a vast library of modules. JavaScript: As web development grows increasingly popular, JavaScript remains a crucial player, with its ability to create dynamic and interactive web pages. Java: This language has stood the test of time and remains a popular choice for enterprise software development. C++: A staple in the gaming and systems development industries, C++ offers exceptional performance and memory management. Swift: Apple's preferred language for iOS app development, Swift continues to grow in popularity with its simplicity and reliability. R: As data science and machin...