Computer-Aided Software
Engineering (CASE) Tools
Computer-aided systems
engineering (CASE) tools are the software programs that help the development
team do their jobs more efficiently and more effectively. These tools support
the drawing and analysis of system models. Some CASE tools also provide prototyping
and code generation capabilities. Some examples are: Oracle’s Designer 2000, Rational’s
Rose, Platinum’s Erwin, Popkin’s System Architect 001, and Visible System’s
Visible Analyst.
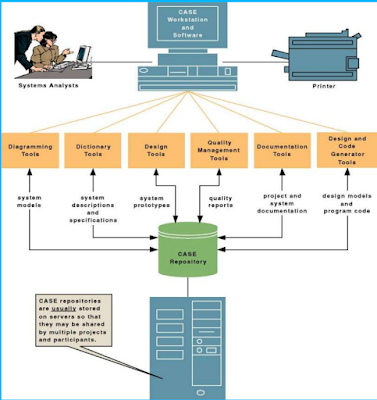
At
the center of any CASE tool’s architecture is a developer’s database called a
CASE repository. CASE repository is a system developer’s database where
developers can store system models, detailed description and specification, and
other products of system development. It is also called dictionary or
encyclopedia.
Around
the CASE repository is a collection of tools or facilities for creating system models
and documentation. These facilities generally include:
- Diagramming tools –These
tools are used to draw system models.
- Dictionary tools – These
tools are used to record, delete, edit, and output detailed documentation and
specification.
- Design tools – These
tools are used to construct system components including system inputs and
outputs. These are also called prototyping tools.
- Documentation tools –
These tools are used to assemble, organize, and report on system models,
descriptions and specifications, and prototypes.
- Quality management tools
– These tools are used to analyze system models, descriptions and specifications,
and prototypes for completeness, consistency, and conformance to accepted rules
of methodologies.
- Design and code generator
tools – These tools automatically generate database designs and application
programs or significant portions of those programs.
Today’s CASE tools
provide two distinct ways to develop system models – forward engineering and
reverse engineering. Forward engineering requires the system analyst to draw
system models, either from scratch or from templates. The resulting models are subsequently
transformed into program code. Reverse engineering, on the other hand, allows a
CASE tool to read existing program code and transform that code into a representative
system model that can be edited and refined by the systems analyst. CASE tools
that allow for bi-directional, forward and reverse engineering are said to
provide for “round-trip engineering”.



Comments
Post a Comment
Subscribe Us and Thanks for visiting blog.