Operators in C Programming: -
An operator in general
is a symbol that operates on a certain data types. An operator is a symbol that
tells the compiler to perform specific mathematical or logical functions.
The types of operators are: -
Arithmetic Operators in C Programming-:
The arithmetic operators performs arithematic
operations. The arithmetic operator is given below:-
(+) - Addition
(-) -Subtraction
(*)- Multiplication
(/)- Division
(%) - Modulo Division
Relational operators in C Programming:-
Relational operators are used to compare logical,
arithmetic and character expression. A list of relational operators is give
below:-
(<) Less than
(>) Greater than
(< =) Less than or equal to
(> =) Greater than or equal to
(==) Equal to
(! =) Not equal to
Logical Operators in C Programming: -
An expression logical operator returns either 0 or 1
depending upon whether expression is used to calculate the value of logical
expression. There are three types of logical operators in C language. They
are:-
(&&) logical AND
(||) Logical OR
(!) Logical NOT
Assignment Operator in C Programming
An assignment operator is used to form an assignment expression,
which assigns the value to an identifier. The most commonly used assignment
operator is = (equal to.). it is written in the form.
Identifier = expression;
Example: - i=100; j=200;
Increment and Decrement operator in C Programming
Increment and decrement operators are unary operators that
add or subtract one form their operands respectively. The increment
operator ++ which adds 1 to its operand and the decrement operator --
which subtracts 1 from its operands.
Conditional Operators in C Programming
Conditional operators which is also called ternary
operator can be used as shorthand for some if-else statements. The operator
consists of two symbols: the question mark (?) and the colon (:).
The general syntax of
the conditional operator is:
Identifier = (test
expression)? Expression 1: Expression 2;
Program
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int
a,b;
printf(" Enter an integer number:\n
");
scanf("%d",&a);
(a%2==0)?printf("\n %d is an even
number.",a):printf("\n %d is an odd number.",a);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT
Size of operators in C Programming
This operator returns the size of its operands in bytes.
The size of operator always precedes its operand. The operand may be an
expression or it may be a cast.
For example, in C programming:
-
i= integer
char= character
printf("Size of
integer :",sizeof(i));
printf("Size of
character:",sizeof(char));
Program:-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int integerType;
float floatType;
double doubleType;
char charType;
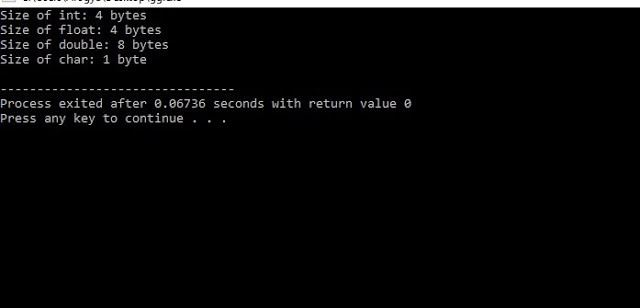
printf("Size of int: %ld bytes\n",sizeof(integerType));
printf("Size of float: %ld bytes\n",sizeof(floatType));
printf("Size of double: %ld
bytes\n",sizeof(doubleType));
printf("Size of char: %ld byte\n",sizeof(charType));
return 0;
}
OUTPUT



Comments
Post a Comment
Subscribe Us and Thanks for visiting blog.